Palette eXtended Kubernetes - Edge
The Palette eXtended Kubernetes - Edge (PXK-E) pack supports Kubernetes clusters set up on Edge hosts installed in isolated locations like grocery stores, restaurants, and similar locations, versus a data center or cloud environment. We offer PXK-E as a core pack in Palette.
PXK and Palette VerteX
The PXK-E used in Palette VerteX is compiled and linked with our NIST-certified FIPS crypto module. PXK-E is by default enabled with Ubuntu Pro with FIPS mode enabled. Additionally, the Operating System (OS) is hardened based on the NIST-800 standard. Refer to the Build Edge Artifacts guide to learn more on how to build the PXK-E image with FIPS mode enabled.
The combined usage of PXK-E and Palette VerteX provides a secure and FIPS-compliant experience as the Kubernetes distribution, OS, and management platform VerteX is FIPS-compliant.
Support Lifecycle
We support PXK-E for N-3 Kubernetes minor versions for a duration of 14 months. The duration exceeds the official EOL by four months. Once we stop supporting the minor version, we initiate the deprecation process. Refer to the Kubernetes Support Lifecycle guide to learn more.
Once you upgrade your cluster to a new Kubernetes version, you will not be able to downgrade. We recommend that, before upgrading, you review the information provided in the Kubernetes Upgrades section.
Review our Maintenance Policy to learn about pack update and deprecation schedules.
Versions Supported
- 1.29.x
- 1.28.x
- 1.27.x
Custom Kubernetes Configuration
The Kubernetes configuration file is where you can do the following:
-
Manually configure a third-party OIDC IDP. For more information, check out Configure Custom OIDC.
-
Add a certificate for the Spectro Proxy pack if you want to use a reverse proxy with a Kubernetes cluster. For more information, refer to the Spectro Proxy guide.
The PXK-E Kubeadm configuration is updated to dynamically enable OIDC based on your IDP selection by adding the
identityProvider parameter.
pack:
palette:
config:
oidc:
identityProvider: <your_idp_selection>
Below is an example of a Kubernetes configuration file.
cluster:
config: |
clusterConfiguration:
apiServer:
extraArgs:
advertise-address: "0.0.0.0"
anonymous-auth: "true"
audit-log-maxage: "30"
audit-log-maxbackup: "10"
audit-log-maxsize: "100"
audit-log-path: /var/log/apiserver/audit.log
audit-policy-file: /etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
authorization-mode: RBAC,Node
default-not-ready-toleration-seconds: "60"
default-unreachable-toleration-seconds: "60"
disable-admission-plugins: AlwaysAdmit
enable-admission-plugins: AlwaysPullImages,NamespaceLifecycle,ServiceAccount,NodeRestriction
profiling: "false"
secure-port: "6443"
tls-cipher-suites: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
extraVolumes:
- hostPath: /var/log/apiserver
mountPath: /var/log/apiserver
name: audit-log
pathType: DirectoryOrCreate
- hostPath: /etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
name: audit-policy
pathType: File
readOnly: true
timeoutForControlPlane: 10m0s
controllerManager:
extraArgs:
feature-gates: RotateKubeletServerCertificate=true
pod-eviction-timeout: 1m0s
profiling: "false"
terminated-pod-gc-threshold: "25"
use-service-account-credentials: "true"
dns: {}
kubernetesVersion: v1.26.4
etcd:
local:
dataDir: "/etc/kubernetes/etcd"
extraArgs:
listen-client-urls: "https://0.0.0.0:2379"
networking:
podSubnet: 192.168.0.0/16
serviceSubnet: 192.169.0.0/16
scheduler:
extraArgs:
profiling: "false"
initConfiguration:
localAPIEndpoint: {}
nodeRegistration:
kubeletExtraArgs:
event-qps: "0"
feature-gates: RotateKubeletServerCertificate=true
protect-kernel-defaults: "true"
read-only-port: "0"
tls-cipher-suites: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
joinConfiguration:
discovery: {}
nodeRegistration:
kubeletExtraArgs:
event-qps: "0"
feature-gates: RotateKubeletServerCertificate=true
protect-kernel-defaults: "true"
read-only-port: "0"
tls-cipher-suites: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
stages:
initramfs:
- sysctl:
vm.overcommit_memory: 1
kernel.panic: 10
kernel.panic_on_oops: 1
commands:
- ln -s /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf /run/kubeconfig
files:
- path: /etc/hosts
permission: "0644"
content: |
127.0.0.1 localhost
- path: "/etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml"
owner_string: "root"
permission: 0600
content: |
apiVersion: audit.k8s.io/v1
kind: Policy
rules:
- level: None
users: ["system:kube-proxy"]
verbs: ["watch"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["endpoints", "services", "services/status"]
- level: None
users: ["system:unsecured"]
namespaces: ["kube-system"]
verbs: ["get"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["configmaps"]
- level: None
users: ["kubelet"] # legacy kubelet identity
verbs: ["get"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["nodes", "nodes/status"]
- level: None
userGroups: ["system:nodes"]
verbs: ["get"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["nodes", "nodes/status"]
- level: None
users:
- system:kube-controller-manager
- system:kube-scheduler
- system:serviceaccount:kube-system:endpoint-controller
verbs: ["get", "update"]
namespaces: ["kube-system"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["endpoints"]
- level: None
users: ["system:apiserver"]
verbs: ["get"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["namespaces", "namespaces/status", "namespaces/finalize"]
- level: None
users: ["cluster-autoscaler"]
verbs: ["get", "update"]
namespaces: ["kube-system"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["configmaps", "endpoints"]
# Don't log HPA fetching metrics.
- level: None
users:
- system:kube-controller-manager
verbs: ["get", "list"]
resources:
- group: "metrics.k8s.io"
# Don't log these read-only URLs.
- level: None
nonResourceURLs:
- /healthz*
- /version
- /swagger*
# Don't log events requests.
- level: None
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["events"]
# node and pod status calls from nodes are high-volume and can be large, don't log responses for expected updates from nodes
- level: Request
users: ["kubelet", "system:node-problem-detector", "system:serviceaccount:kube-system:node-problem-detector"]
verbs: ["update","patch"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["nodes/status", "pods/status"]
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
- level: Request
userGroups: ["system:nodes"]
verbs: ["update","patch"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["nodes/status", "pods/status"]
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# deletecollection calls can be large, don't log responses for expected namespace deletions
- level: Request
users: ["system:serviceaccount:kube-system:namespace-controller"]
verbs: ["deletecollection"]
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# Secrets, ConfigMaps, and TokenReviews can contain sensitive & binary data,
# so only log at the Metadata level.
- level: Metadata
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["secrets", "configmaps"]
- group: authentication.k8s.io
resources: ["tokenreviews"]
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# Get repsonses can be large; skip them.
- level: Request
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
- group: "admissionregistration.k8s.io"
- group: "apiextensions.k8s.io"
- group: "apiregistration.k8s.io"
- group: "apps"
- group: "authentication.k8s.io"
- group: "authorization.k8s.io"
- group: "autoscaling"
- group: "batch"
- group: "certificates.k8s.io"
- group: "extensions"
- group: "metrics.k8s.io"
- group: "networking.k8s.io"
- group: "policy"
- group: "rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
- group: "settings.k8s.io"
- group: "storage.k8s.io"
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# Default level for known APIs
- level: RequestResponse
resources:
- group: "" # core
- group: "admissionregistration.k8s.io"
- group: "apiextensions.k8s.io"
- group: "apiregistration.k8s.io"
- group: "apps"
- group: "authentication.k8s.io"
- group: "authorization.k8s.io"
- group: "autoscaling"
- group: "batch"
- group: "certificates.k8s.io"
- group: "extensions"
- group: "metrics.k8s.io"
- group: "networking.k8s.io"
- group: "policy"
- group: "rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
- group: "settings.k8s.io"
- group: "storage.k8s.io"
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# Default level for all other requests.
- level: Metadata
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
pack:
palette:
config:
oidc:
identityProvider: palette
Configure OIDC Identity Provider
The OIDC IDP feature offers the convenience of managing OIDC at the Kubernetes layer. The OIDC IDP feature is particularly useful for environments that do not have their own IDP configured. In this scenario, you can leverage Palette as an IDP without having to configure a third-party IDP. We also support the ability to take advantage of other OIDC providers by making it possible for you to configure OIDC at the tenant level. For additional flexibility, if you wish to use a different IDP than the one configured at the tenant level, you can select a different IDP by adding the OIDC configuration to your cluster profile.
When you add the PXK-E pack to a cluster profile, Palette displays the OIDC IDP options listed below.
All the options require you to map a set of users or groups to a Kubernetes RBAC role. To learn how to map a Kubernetes role to users and groups, refer to Create Role Bindings.
You can create a role binding that maps individual users or groups assigned within the OIDC provider's configuration to a role. To learn more, review Use RBAC with OIDC. You can also configure OIDC for virtual clusters. For guidance, refer to Configure OIDC for a Virtual Cluster.
-
None: This setting does not require OIDC configuration for the cluster. It displays in the YAML file as
noauth. -
Custom: This is the default setting and does not require OIDC configuration. However, if desired, it allows you to specify a third-party OIDC provider by configuring OIDC statements in the YAML file as described in Configure Custom OIDC. This setting displays in the YAML file as
none. -
Palette: This setting makes Palette the IDP. Any user with a Palette account in the tenant and the proper permissions to view and access the project's resources is able to log into the Kubernetes dashboard. This setting displays in the YAML file as
palette. -
Inherit from Tenant: This setting allows you to apply RBAC to multiple clusters and requires you to configure OpenID Connect (OIDC) in Tenant Settings. In Tenant Admin scope, navigate to Tenant Settings > SSO, choose OIDC, and provide your third-party IDP details. This setting displays in the YAML file as
tenant. For more information, check out the SSO Setup guide.
If your IDP uses Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) authentication, then the Inherit from Tenant option will not work, and you will need to use the Custom option instead. This is because Kubernetes supports only OIDC authentication and not SAML authentication.
Configure Custom OIDC
Follow these steps to configure a third-party OIDC IDP.
-
Add the following OIDC parameters to the
apiServer.extraArgssection of your Kubernetes YAML file when creating a cluster profile.cluster:
config: |
clusterConfiguration:
apiServer:
extraArgs:
oidc-issuer-url: "provider URL"
oidc-client-id: "client-id"
oidc-groups-claim: "groups"
oidc-username-claim: "email" -
Add the following
clientConfigsection that contains OIDC parameters to your Kubernetes configuration file.clientConfig:
oidc-issuer-url: "<OIDC-ISSUER-URL>"
oidc-client-id: "<OIDC-CLIENT-ID>"
oidc-client-secret: "<OIDC-CLIENT-SECRET>"
oidc-extra-scope: profile,email,openid -
Provide third-party OIDC IDP details.
Use RBAC with OIDC
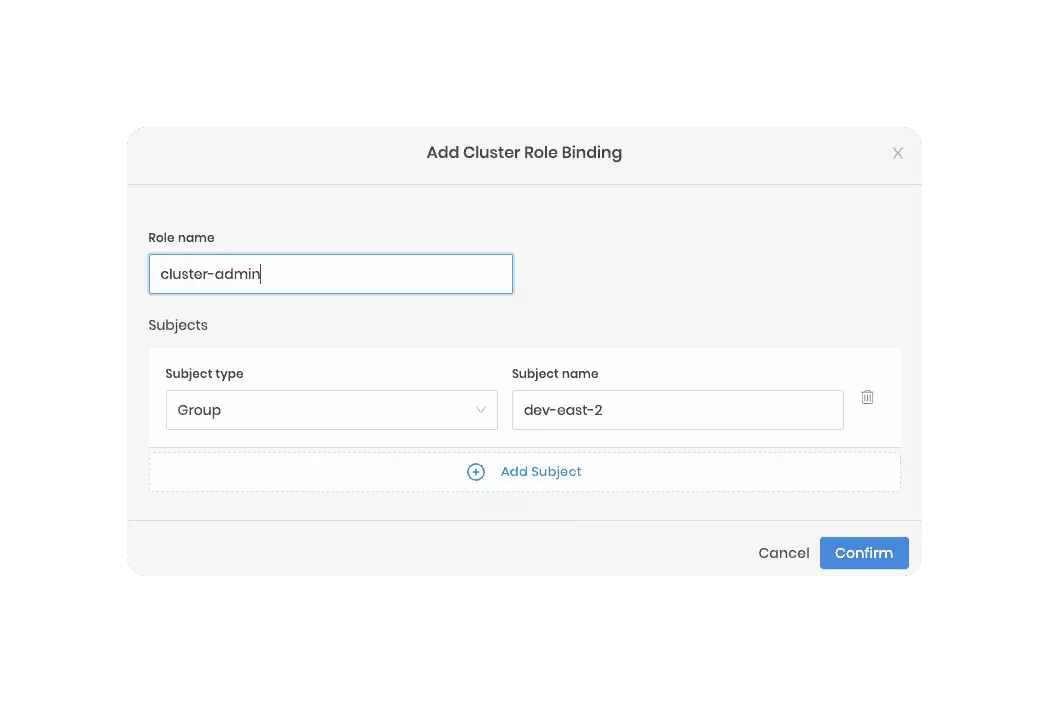
You can create a role binding that uses individual users as the subject or specify a group name as the subject to map many users to a role. The group name is the group assigned in the OIDC provider's configuration. Below is an example. To learn more, review Create Role Bindings.
Assume you created a group named dev-east-2 within an OIDC provider. If you configure the host cluster's Kubernetes
pack with all the correct OIDC settings, you could then create a role binding for the dev-east-2 group.
In this example, Palette is used as the IDP, and all users in the dev-east-2 would inherit the cluster-admin role.
Custom Kubernetes Configuration
The Kubernetes configuration file is where you can do the following:
-
Manually configure a third-party OIDC IDP. For more information, check out Configure Custom OIDC.
-
Add a certificate for the Spectro Proxy pack if you want to use a reverse proxy with a Kubernetes cluster. For more information, refer to the Spectro Proxy guide.
The PXK-E Kubeadm configuration is updated to dynamically enable OIDC based on your IDP selection by adding the
identityProvider parameter.
pack:
palette:
config:
oidc:
identityProvider: <your_idp_selection>
Below is an example of a Kubernetes configuration file.
cluster:
config: |
clusterConfiguration:
apiServer:
extraArgs:
advertise-address: "0.0.0.0"
anonymous-auth: "true"
audit-log-maxage: "30"
audit-log-maxbackup: "10"
audit-log-maxsize: "100"
audit-log-path: /var/log/apiserver/audit.log
audit-policy-file: /etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
authorization-mode: RBAC,Node
default-not-ready-toleration-seconds: "60"
default-unreachable-toleration-seconds: "60"
disable-admission-plugins: AlwaysAdmit
enable-admission-plugins: AlwaysPullImages,NamespaceLifecycle,ServiceAccount,NodeRestriction
profiling: "false"
secure-port: "6443"
tls-cipher-suites: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
extraVolumes:
- hostPath: /var/log/apiserver
mountPath: /var/log/apiserver
name: audit-log
pathType: DirectoryOrCreate
- hostPath: /etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
name: audit-policy
pathType: File
readOnly: true
timeoutForControlPlane: 10m0s
controllerManager:
extraArgs:
feature-gates: RotateKubeletServerCertificate=true
pod-eviction-timeout: 1m0s
profiling: "false"
terminated-pod-gc-threshold: "25"
use-service-account-credentials: "true"
dns: {}
kubernetesVersion: v1.26.4
etcd:
local:
dataDir: "/etc/kubernetes/etcd"
extraArgs:
listen-client-urls: "https://0.0.0.0:2379"
networking:
podSubnet: 192.168.0.0/16
serviceSubnet: 192.169.0.0/16
scheduler:
extraArgs:
profiling: "false"
initConfiguration:
localAPIEndpoint: {}
nodeRegistration:
kubeletExtraArgs:
event-qps: "0"
feature-gates: RotateKubeletServerCertificate=true
protect-kernel-defaults: "true"
read-only-port: "0"
tls-cipher-suites: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
joinConfiguration:
discovery: {}
nodeRegistration:
kubeletExtraArgs:
event-qps: "0"
feature-gates: RotateKubeletServerCertificate=true
protect-kernel-defaults: "true"
read-only-port: "0"
tls-cipher-suites: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
stages:
initramfs:
- sysctl:
vm.overcommit_memory: 1
kernel.panic: 10
kernel.panic_on_oops: 1
commands:
- ln -s /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf /run/kubeconfig
files:
- path: /etc/hosts
permission: "0644"
content: |
127.0.0.1 localhost
- path: "/etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml"
owner_string: "root"
permission: 0600
content: |
apiVersion: audit.k8s.io/v1
kind: Policy
rules:
- level: None
users: ["system:kube-proxy"]
verbs: ["watch"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["endpoints", "services", "services/status"]
- level: None
users: ["system:unsecured"]
namespaces: ["kube-system"]
verbs: ["get"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["configmaps"]
- level: None
users: ["kubelet"] # legacy kubelet identity
verbs: ["get"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["nodes", "nodes/status"]
- level: None
userGroups: ["system:nodes"]
verbs: ["get"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["nodes", "nodes/status"]
- level: None
users:
- system:kube-controller-manager
- system:kube-scheduler
- system:serviceaccount:kube-system:endpoint-controller
verbs: ["get", "update"]
namespaces: ["kube-system"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["endpoints"]
- level: None
users: ["system:apiserver"]
verbs: ["get"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["namespaces", "namespaces/status", "namespaces/finalize"]
- level: None
users: ["cluster-autoscaler"]
verbs: ["get", "update"]
namespaces: ["kube-system"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["configmaps", "endpoints"]
# Don't log HPA fetching metrics.
- level: None
users:
- system:kube-controller-manager
verbs: ["get", "list"]
resources:
- group: "metrics.k8s.io"
# Don't log these read-only URLs.
- level: None
nonResourceURLs:
- /healthz*
- /version
- /swagger*
# Don't log events requests.
- level: None
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["events"]
# node and pod status calls from nodes are high-volume and can be large, don't log responses for expected updates from nodes
- level: Request
users: ["kubelet", "system:node-problem-detector", "system:serviceaccount:kube-system:node-problem-detector"]
verbs: ["update","patch"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["nodes/status", "pods/status"]
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
- level: Request
userGroups: ["system:nodes"]
verbs: ["update","patch"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["nodes/status", "pods/status"]
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# deletecollection calls can be large, don't log responses for expected namespace deletions
- level: Request
users: ["system:serviceaccount:kube-system:namespace-controller"]
verbs: ["deletecollection"]
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# Secrets, ConfigMaps, and TokenReviews can contain sensitive & binary data,
# so only log at the Metadata level.
- level: Metadata
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["secrets", "configmaps"]
- group: authentication.k8s.io
resources: ["tokenreviews"]
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# Get repsonses can be large; skip them.
- level: Request
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
- group: "admissionregistration.k8s.io"
- group: "apiextensions.k8s.io"
- group: "apiregistration.k8s.io"
- group: "apps"
- group: "authentication.k8s.io"
- group: "authorization.k8s.io"
- group: "autoscaling"
- group: "batch"
- group: "certificates.k8s.io"
- group: "extensions"
- group: "metrics.k8s.io"
- group: "networking.k8s.io"
- group: "policy"
- group: "rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
- group: "settings.k8s.io"
- group: "storage.k8s.io"
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# Default level for known APIs
- level: RequestResponse
resources:
- group: "" # core
- group: "admissionregistration.k8s.io"
- group: "apiextensions.k8s.io"
- group: "apiregistration.k8s.io"
- group: "apps"
- group: "authentication.k8s.io"
- group: "authorization.k8s.io"
- group: "autoscaling"
- group: "batch"
- group: "certificates.k8s.io"
- group: "extensions"
- group: "metrics.k8s.io"
- group: "networking.k8s.io"
- group: "policy"
- group: "rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
- group: "settings.k8s.io"
- group: "storage.k8s.io"
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# Default level for all other requests.
- level: Metadata
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
pack:
palette:
config:
oidc:
identityProvider: palette
Configure OIDC Identity Provider
The OIDC IDP feature offers the convenience of managing OIDC at the Kubernetes layer. The OIDC IDP feature is particularly useful for environments that do not have their own IDP configured. In this scenario, you can leverage Palette as an IDP without having to configure a third-party IDP. We also support the ability to take advantage of other OIDC providers by making it possible for you to configure OIDC at the tenant level. For additional flexibility, if you wish to use a different IDP than the one configured at the tenant level, you can select a different IDP by adding the OIDC configuration to your cluster profile.
When you add the PXK-E pack to a cluster profile, Palette displays the OIDC IDP options listed below.
All the options require you to map a set of users or groups to a Kubernetes RBAC role. To learn how to map a Kubernetes role to users and groups, refer to Create Role Bindings.
You can create a role binding that maps individual users or groups assigned within the OIDC provider's configuration to a role. To learn more, review Use RBAC with OIDC. You can also configure OIDC for virtual clusters. For guidance, refer to Configure OIDC for a Virtual Cluster.
-
None: This setting does not require OIDC configuration for the cluster. It displays in the YAML file as
noauth. -
Custom: This is the default setting and does not require OIDC configuration. However, if desired, it allows you to specify a third-party OIDC provider by configuring OIDC statements in the YAML file as described in Configure Custom OIDC. This setting displays in the YAML file as
none. -
Palette: This setting makes Palette the IDP. Any user with a Palette account in the tenant and the proper permissions to view and access the project's resources is able to log into the Kubernetes dashboard. This setting displays in the YAML file as
palette. -
Inherit from Tenant: This setting allows you to apply RBAC to multiple clusters and requires you to configure OpenID Connect (OIDC) in Tenant Settings. In Tenant Admin scope, navigate to Tenant Settings > SSO, choose OIDC, and provide your third-party IDP details. This setting displays in the YAML file as
tenant. For more information, check out the SSO Setup guide.
If your IDP uses Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) authentication, then the Inherit from Tenant option will not work, and you will need to use the Custom option instead. This is because Kubernetes supports only OIDC authentication and not SAML authentication.
Configure Custom OIDC
Follow these steps to configure a third-party OIDC IDP.
-
Add the following OIDC parameters to the
apiServer.extraArgssection of your Kubernetes YAML file when creating a cluster profile.cluster:
config: |
clusterConfiguration:
apiServer:
extraArgs:
oidc-issuer-url: "provider URL"
oidc-client-id: "client-id"
oidc-groups-claim: "groups"
oidc-username-claim: "email" -
Add the following
clientConfigsection that contains OIDC parameters to your Kubernetes configuration file.clientConfig:
oidc-issuer-url: "<OIDC-ISSUER-URL>"
oidc-client-id: "<OIDC-CLIENT-ID>"
oidc-client-secret: "<OIDC-CLIENT-SECRET>"
oidc-extra-scope: profile,email,openid -
Provide third-party OIDC IDP details.
Use RBAC with OIDC
You can create a role binding that uses individual users as the subject or specify a group name as the subject to map many users to a role. The group name is the group assigned in the OIDC provider's configuration. Below is an example. To learn more, review Create Role Bindings.
Assume you created a group named dev-east-2 within an OIDC provider. If you configure the host cluster's Kubernetes
pack with all the correct OIDC settings, you could then create a role binding for the dev-east-2 group.
In this example, Palette is used as the IDP, and all users in the dev-east-2 would inherit the cluster-admin role.

Custom Kubernetes Configuration
The Kubernetes configuration file is where you can do the following:
-
Manually configure a third-party OIDC IDP. For more information, check out Configure Custom OIDC.
-
Add a certificate for the Spectro Proxy pack if you want to use a reverse proxy with a Kubernetes cluster. For more information, refer to the Spectro Proxy guide.
The PXK-E Kubeadm configuration is updated to dynamically enable OIDC based on your IDP selection by adding the
identityProvider parameter.
pack:
palette:
config:
oidc:
identityProvider: <your_idp_selection>
Below is an example of a Kubernetes configuration file.
cluster:
config: |
clusterConfiguration:
apiServer:
extraArgs:
advertise-address: "0.0.0.0"
anonymous-auth: "true"
audit-log-maxage: "30"
audit-log-maxbackup: "10"
audit-log-maxsize: "100"
audit-log-path: /var/log/apiserver/audit.log
audit-policy-file: /etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
authorization-mode: RBAC,Node
default-not-ready-toleration-seconds: "60"
default-unreachable-toleration-seconds: "60"
disable-admission-plugins: AlwaysAdmit
enable-admission-plugins: AlwaysPullImages,NamespaceLifecycle,ServiceAccount,NodeRestriction
profiling: "false"
secure-port: "6443"
tls-cipher-suites: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
extraVolumes:
- hostPath: /var/log/apiserver
mountPath: /var/log/apiserver
name: audit-log
pathType: DirectoryOrCreate
- hostPath: /etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
name: audit-policy
pathType: File
readOnly: true
timeoutForControlPlane: 10m0s
controllerManager:
extraArgs:
feature-gates: RotateKubeletServerCertificate=true
pod-eviction-timeout: 1m0s
profiling: "false"
terminated-pod-gc-threshold: "25"
use-service-account-credentials: "true"
dns: {}
kubernetesVersion: v1.26.4
etcd:
local:
dataDir: "/etc/kubernetes/etcd"
extraArgs:
listen-client-urls: "https://0.0.0.0:2379"
networking:
podSubnet: 192.168.0.0/16
serviceSubnet: 192.169.0.0/16
scheduler:
extraArgs:
profiling: "false"
initConfiguration:
localAPIEndpoint: {}
nodeRegistration:
kubeletExtraArgs:
event-qps: "0"
feature-gates: RotateKubeletServerCertificate=true
protect-kernel-defaults: "true"
read-only-port: "0"
tls-cipher-suites: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
joinConfiguration:
discovery: {}
nodeRegistration:
kubeletExtraArgs:
event-qps: "0"
feature-gates: RotateKubeletServerCertificate=true
protect-kernel-defaults: "true"
read-only-port: "0"
tls-cipher-suites: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
stages:
initramfs:
- sysctl:
vm.overcommit_memory: 1
kernel.panic: 10
kernel.panic_on_oops: 1
commands:
- ln -s /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf /run/kubeconfig
files:
- path: /etc/hosts
permission: "0644"
content: |
127.0.0.1 localhost
- path: "/etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml"
owner_string: "root"
permission: 0600
content: |
apiVersion: audit.k8s.io/v1
kind: Policy
rules:
- level: None
users: ["system:kube-proxy"]
verbs: ["watch"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["endpoints", "services", "services/status"]
- level: None
users: ["system:unsecured"]
namespaces: ["kube-system"]
verbs: ["get"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["configmaps"]
- level: None
users: ["kubelet"] # legacy kubelet identity
verbs: ["get"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["nodes", "nodes/status"]
- level: None
userGroups: ["system:nodes"]
verbs: ["get"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["nodes", "nodes/status"]
- level: None
users:
- system:kube-controller-manager
- system:kube-scheduler
- system:serviceaccount:kube-system:endpoint-controller
verbs: ["get", "update"]
namespaces: ["kube-system"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["endpoints"]
- level: None
users: ["system:apiserver"]
verbs: ["get"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["namespaces", "namespaces/status", "namespaces/finalize"]
- level: None
users: ["cluster-autoscaler"]
verbs: ["get", "update"]
namespaces: ["kube-system"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["configmaps", "endpoints"]
# Don't log HPA fetching metrics.
- level: None
users:
- system:kube-controller-manager
verbs: ["get", "list"]
resources:
- group: "metrics.k8s.io"
# Don't log these read-only URLs.
- level: None
nonResourceURLs:
- /healthz*
- /version
- /swagger*
# Don't log events requests.
- level: None
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["events"]
# node and pod status calls from nodes are high-volume and can be large, don't log responses for expected updates from nodes
- level: Request
users: ["kubelet", "system:node-problem-detector", "system:serviceaccount:kube-system:node-problem-detector"]
verbs: ["update","patch"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["nodes/status", "pods/status"]
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
- level: Request
userGroups: ["system:nodes"]
verbs: ["update","patch"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["nodes/status", "pods/status"]
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# deletecollection calls can be large, don't log responses for expected namespace deletions
- level: Request
users: ["system:serviceaccount:kube-system:namespace-controller"]
verbs: ["deletecollection"]
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# Secrets, ConfigMaps, and TokenReviews can contain sensitive & binary data,
# so only log at the Metadata level.
- level: Metadata
resources:
- group: "" # core
resources: ["secrets", "configmaps"]
- group: authentication.k8s.io
resources: ["tokenreviews"]
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# Get repsonses can be large; skip them.
- level: Request
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
resources:
- group: "" # core
- group: "admissionregistration.k8s.io"
- group: "apiextensions.k8s.io"
- group: "apiregistration.k8s.io"
- group: "apps"
- group: "authentication.k8s.io"
- group: "authorization.k8s.io"
- group: "autoscaling"
- group: "batch"
- group: "certificates.k8s.io"
- group: "extensions"
- group: "metrics.k8s.io"
- group: "networking.k8s.io"
- group: "policy"
- group: "rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
- group: "settings.k8s.io"
- group: "storage.k8s.io"
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# Default level for known APIs
- level: RequestResponse
resources:
- group: "" # core
- group: "admissionregistration.k8s.io"
- group: "apiextensions.k8s.io"
- group: "apiregistration.k8s.io"
- group: "apps"
- group: "authentication.k8s.io"
- group: "authorization.k8s.io"
- group: "autoscaling"
- group: "batch"
- group: "certificates.k8s.io"
- group: "extensions"
- group: "metrics.k8s.io"
- group: "networking.k8s.io"
- group: "policy"
- group: "rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
- group: "settings.k8s.io"
- group: "storage.k8s.io"
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
# Default level for all other requests.
- level: Metadata
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
pack:
palette:
config:
oidc:
identityProvider: palette
Configure OIDC Identity Provider
The OIDC IDP feature offers the convenience of managing OIDC at the Kubernetes layer. The OIDC IDP feature is particularly useful for environments that do not have their own IDP configured. In this scenario, you can leverage Palette as an IDP without having to configure a third-party IDP. We also support the ability to take advantage of other OIDC providers by making it possible for you to configure OIDC at the tenant level. For additional flexibility, if you wish to use a different IDP than the one configured at the tenant level, you can select a different IDP by adding the OIDC configuration to your cluster profile.
When you add the PXK-E pack to a cluster profile, Palette displays the OIDC IDP options listed below.
All the options require you to map a set of users or groups to a Kubernetes RBAC role. To learn how to map a Kubernetes role to users and groups, refer to Create Role Bindings.
You can create a role binding that maps individual users or groups assigned within the OIDC provider's configuration to a role. To learn more, review
Use RBAC with OIDC. You can also configure OIDC for virtual clusters. For guidance, refer to Configure OIDC for a Virtual Cluster.
-
None: This setting does not require OIDC configuration for the cluster. It displays in the YAML file as
noauth. -
Custom: This is the default setting and does not require OIDC configuration. However, if desired, it allows you to specify a third-party OIDC provider by configuring OIDC statements in the YAML file as described in
Configure Custom OIDC. This setting displays in the YAML file as
none. -
Palette: This setting makes Palette the IDP. Any user with a Palette account in the tenant and the proper permissions to view and access the project's resources is able to log into the Kubernetes dashboard. This setting displays in the YAML file as
palette. -
Inherit from Tenant: This setting allows you to apply RBAC to multiple clusters and requires you to configure OpenID Connect (OIDC) in Tenant Settings. In Tenant Admin scope, navigate to Tenant Settings > SSO, choose OIDC, and provide your third-party IDP details. This setting displays in the YAML file as
tenant. For more information, check out the SSO Setup guide.
If your IDP uses Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) authentication, then the Inherit from Tenant option will not work, and you will need to use the Custom option instead. This is because Kubernetes supports only OIDC authentication and not SAML authentication.
Configure Custom OIDC
Follow these steps to configure a third-party OIDC IDP.
-
Add the following OIDC parameters to the
apiServer.extraArgssection of your Kubernetes YAML file when creating a cluster profile.cluster:
config:
clusterConfiguration:
apiServer:
extraArgs:
oidc-issuer-url: "provider URL"
oidc-client-id: "client-id"
oidc-groups-claim: "groups"
oidc-username-claim: "email" -
Add the following
kubeadmconfig.clientConfigsection that contains OIDC parameters to your Kubernetes YAML file.kubeadmconfig:
clientConfig:
oidc-issuer-url: "<OIDC-ISSUER-URL>"
oidc-client-id: "<OIDC-CLIENT-ID>"
oidc-client-secret: "<OIDC-CLIENT-SECRET>"
oidc-extra-scope: profile,email,openid -
Provide third-party OIDC IDP details.
Use RBAC with OIDC
You can create a role binding that uses individual users as the subject or specify a group name as the subject to map many users to a role. The group name is the group assigned in the OIDC provider's configuration. Below is an example. To learn more, review Create Role Bindings.
Assume you created a group named dev-east-2 within an OIDC provider. If you configure the host cluster's Kubernetes
pack with all the correct OIDC settings, you could then create a role binding for the dev-east-2 group.
In this example, Palette is used as the IDP, and all users in the dev-east-2 would inherit the cluster-admin role.

Terraform
You can reference Kubernetes in Terraform with the following code snippet.
data "spectrocloud_registry" "public_registry" {
name = "Public Repo"
}
data "spectrocloud_pack_simple" "edge-k8s" {
name = "edge-k8s"
version = "1.29.0"
type = "helm"
registry_uid = data.spectrocloud_registry.public_registry.id
}